MCQ on AC Circuits
MCQ on AC Circuits, Alternating Current MCQ, MCQ on Alternating Current, Multiple Choice Questions on MCQ on AC Circuits, Engineering MCQ, Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. A current is said to be direct current when its
- magnitude remains constant with time
- magnitude changes with time
- direction changes with time
- magnitude and direction changes with time
Answer: magnitude remains constant with time
Q.2. A current is said to be alternating when it changes in
- magnitude only
- direction only
- both magnitude and direction
- none of the above
Answer: both magnitude and direction
Q.3. The standard supply frequency in India is
- 25 Hz
- 50 Hz
- 60 Hz
- 100 Hz
Answer: 50 Hz
Q.4. The angular frequency of an alternating quantity is a mathematical quantity obtained by multiplying the frequency f of the alternating quantity by a factor
- π/2
- π
- 2 π
- 4 π
Answer: 2 π
Q.5. A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The RMS value of current is
- 2.8 A
- about 2 A
- 1.4 A
- Undefined
Answer: 2.8 A
Q.6. The ratio of effective value to average value is called the …. factor.
- form
- peak
- average
- Q-factor
Answer: form
Q.7. The RMS value of a sine wave is 100 A. Its peak value is
- 70.7 A
- 141 A
- 150 A
- 282.8 A
Answer: 141 A
Q.8. When the two quantities are in quadrature the phase angle between them will be
- 45° or π/4 radians
- 90° or π/2 radians
- 135° or 3π/4 radians
- 60° or π/3 radians
Answer: 90° or π/2 radians
Q.9. In ac circuits the power curve is a sine wave having
- same frequency as that of voltage
- double the frequency of the voltage
- half the frequency of the voltage
- none of the above
Answer: double the frequency of the voltage
Q.10. Electrical power converted into heat due to the flow of an alternating current through an ohmic resistance is called the …….. power.
- heating
- true
- reactive
- apparent
Answer: true
Q.11. Average power in a purely resistive circuit is equal to
- zero
- product of average values of current and voltage
- product of peak values of current and voltage
- product of rms or effective values of current and voltage
Answer: product of RMS or effective values of current and voltage
Q.12. If an alternating triangular voltage is applied to a resistor, the shape of the current waveform will be ……. waveform.
- triangular
- sawtooth
- sinusoidal
- square
Answer: triangular
Q.13. The purely inductive circuit takes power from the ac mains when
- both applied voltage and current increase
- both applied voltage and current decrease
- applied voltage decreases but current increases
- applied voltage increases but current decreases
Answer: applied voltage decreases but current increases
Q.14. Which of the following statements associated with a purely capacitive circuit is not true?
- Power consumed is zero.
- Heat produced is zero.
- Power factor is unity.
- Work done is zero.
- Power factor is zero.
Answer: Power factor is unity.
Q.15. A two-terminal black box contains a series combination of a resistor and an unknown two-terminal linear device. As soon as the battery is connected to the black box the current is found to be zero. The device is
- an inductor
- a capacitor
- a resistor
- an unknown
Answer: an inductor
Q.16. The reactance offered by a capacitor to alternating current of frequency 50 Hz is 10 Ω. If the frequency is increased to 100 Hz, reactance becomes:
- 20 ohms
- 5 ohms
- 2.5 ohms
- 40 ohms
Answer: 5 ohms
Q.17. The apparent power and active power is drawn are equal for an ac circuit of:
- inductive type
- capacitive type
- resistive type
- none of these
Answer: resistive type
Q.18. When a sinusoidal voltage is applied across R-L series circuit having R = XL, the phase angle will be:
- 90°
- 45° lag
- 45° leading
- 90° leading
Answer: 45° leading
Q.19. In a series R-L circuit
- voltage drops across R and L are in phase
- voltage drop across L leads the voltage drop across R by 90°
- voltage drop across L lags behind the voltage drop across R by 90°
- voltage drops across R and L are in phase opposition
Answer: voltage drop across L leads the voltage drop across R by 90°
Q.20. In an ac circuit, the applied voltage and current drawn are represented as v = Vmax sin ωt and i = Imax sin (ωt + ϕ). The pf of the circuit is
- sin ϕ
- cos ϕ (lagging)
- cos ϕ (leading)
- none of these
Answer: cos ϕ (leading)
Q.21. Q-factor of a coil is the measure of its
- selectivity
- retentivity
- resistivity
- self inductance
Answer: selectivity
Q.22. In a series R-C circuit current …….. with the increase in frequency.
- increases
- decreases
- remains unaltered
- None of the above
Answer: increases
Q.23. A 100 W, 100 V bulb is to be supplied from 220 V, 50 Hz supply. Which of the following arrangements is preferable?
- Additional pure inductance in series with lamp.
- Additional resistance in series with the lamp.
- Additional inductance and capacitance in series with the lamp.
- None of the above
Answer: Additional pure inductance in series with the lamp.
Q.24. The source in the circuit shown is a sinusoidal source. The supply voltage across various elements is marked in the figure. The input voltage is
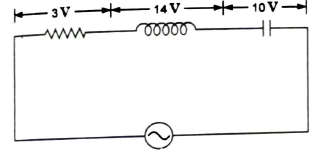
- 10 V
- 5 V
- 27 V
- 24 V
Answer: 5 V
Q.25. If a series RLC circuit is excited by a voltage e = E sin ωt where LC < 1/ω2
- current lags behind the applied voltage
- current leads the applied voltage
- current is in phase with the applied voltage
- voltage across L and C are equal
Answer: current leads the applied voltage