Discrete Convolution and Correlation MCQ
Discrete Convolution and Correlation MCQ, Multiple Choice Questions on Discrete Convolution and Correlation, Discrete Convolution MCQ, Discrete Correlation MCQ, Digital Signal Processing MCQ, DSP MCQ, Engineering MCQ
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems MCQ
Objective Type Questions
Q.1. The commutative property of convolution states that
- x(n) *h(n) = h(n) *x(n)
- [ x(n) *h1 (n)] *h2 (n) = x(n) * [h1 (n) *h2 (n)]
- x(n) * [h1(n) + h2 (n)] = x(n) *h1(n) + x(n) *h2 (n)
- none of these
Answer: x(n) *h(n) = h(n) *x(n)
Q.2. The associate property of convolution states that
- x(n) *h(n) = h(n) *x(n)
- [x(n) *h1 (n)] *h2 (n) = x(n) * [h1 (n) *h2 (n)]
- x(n) * [h1(n) + h2 (n)] = x(n) *h1(n) + x(n) *h2 (n)
- none of these
Answer: [ x(n) *h1 (n)] *h2 (n) = x(n) * [h1 (n) *h2 (n)]
Q.3. The distributive property of convolution states that
- x(n) *h(n) = h(n) *x(n)
- [ x(n) *h1 (n)] *h2 (n) = x(n) * [h1 (n) *h2 (n)]
- x(n) * [h1(n) + h2 (n)] = x(n) *h1(n) + x(n) *h2 (n)
- none of these
Answer: x(n) * [h1(n) + h2 (n)] = x(n) *h1(n) + x(n) *h2 (n)
Q.4. For a non-causal system h(n) excited by a non-causal input x(n), the output y(n) is given by
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Answer: y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
Q.5. For a non-causal system h(n) excited by a causal input x(n), the output y(n) is given by
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Answer: y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
Q.6. For a causal system h(n) excited by a non-causal input x(n), the output y(n) is given by
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Answer: y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Q.7. For a causal system h(n) excited by a causal input x(n), the output y(n) is given by
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{\infty }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
- y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Answer: y(n)=\sum_{k=0 }^{n }x(k)h(n-k)
Q.8. If x(n) = {1, 2, 3, 0} and h(n) = {3, 1, 0, 0, 0}, the length of y(n) = x(n) * h(n) is
- 8
- 7
- 9
- none of these
Answer: 8
Q.9. {1, 2, 3} * {3, 2, 1} =
- {3, 8, 1, 4, 8, 3}
- {3, 8, 8, 3}
- {3, 8, 12, 8, 3}
- {2, 3, 8, 14, 8, 3}
Answer: {3, 8, 1, 4, 8, 3}
Q.10.
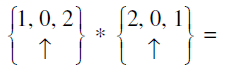
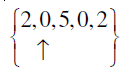
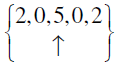
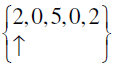
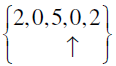
Answer:
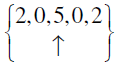
Q.11. [x(n) = {δ (n +2) - δ (n) + δ (n -2)}] *[h(n) = { δ (n) + δ (n -1)}] is

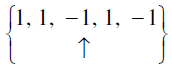

none of these
Answer:

Q.12. The convolution of x(n) = {1, 2, 0, 0, 0} and h(n) = {2, 1, 0} is
- {2, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0}
- {2, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0}
- {2, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
- {2, 5, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}
Answer: {2, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0}
Q.13. If x(n) = {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6}, then circularly shifted signal x(n – 2) =
- {0, 6, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4}
- {0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4}
- {0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6}
- {-1, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 4}
Answer: {0, 6, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4}
Q.14. If x(n) = {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6}, then circularly shifted signal x(n + 2) =
- {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6, 0, 0}
- {3, 0, 4, 0, 6, 1, 2}
- {3, 4, 5, 0, 6, 0, 8}
- {0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6}
Answer: {3, 0, 4, 0, 6, 1, 2}
Q15. If x(n) = {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 0, 6}, then circularly flipped signal x(–n) =
- {1, 6, 0, 4, 0, 3, 2, 1}
- {6, 0, 4, 0, 3, 2, 1}
- {-1, -2, -3, 0, -4, 0, -6}
- none of these
Answer: {1, 6, 0, 4, 0, 3, 2, 1}
Q.16. The circular convolution of x(n) = {1, 2, 1} and h(n) = {2, 1, 2} is
- {7, 7, 6}
- {6, 7, 6}
- {6, 7, 6, 0}
- {0, 7, 7, 6}
Answer: {7, 7, 6}
Q.17. What is the periodic extension of x(n) = {1,0,2,0,3,0,4} for period N = 3?
- {2, 3, 5}
- {5, 3, 2}
- {1, 2, 3}
- {1, 0, 2}
Answer: {5, 3, 2}
Q.18. What is the periodic extension of x(n) = {2, 2} for N = 3?
- {2, 2, 0}
- {0, 2, 2}
- {2, 2, 2}
- {0, 2, 2, 0}
Answer: {2, 2, 0}
Q.19. The cross correlation of x(n) = {1, 2, 1} and h(n) = {1, 2} is
- {1, 4, 5, 2}
- {2, 5, 4, 1}
- {1, 2, 1, 1, 2}
- {1, 3, 5, 2}
Answer: {2, 5, 4, 1}
Q.20. The autocorrelation of x(n) = {2, 1} is
- {2, 5, 2}
- {4, 4, 1}
- {2, 1}
- {2, 1, 2, 1}
Answer: {2, 5, 2}
Thank you for this post.